How Long Does THC Stay in Your Body and Impact Real-World Driving Ability?
How long does THC stay in your body, and more importantly, how long does it actually impair your ability to drive? Some experts imply that residual effects of cannabis such as a decrease in recall, learning, and memory would significantly impair driving ability and thus if someone “smokes cannabis” that they should not operate a motor vehicle for 24 to 48 hours and even 28 days later.
Understanding THC Detection vs. Actual Impairment
The question of how long does THC stay in your body involves two distinct considerations: detection windows and functional impairment windows. Forensic toxicologist James Wigmore‘s extensive research on THC detection windows and impairment markers reveals that THC metabolites can remain detectable in biological samples far longer than they cause measurable impairment.
THC detection timeframes vary dramatically depending on the biological matrix tested:
- Oral fluid: Active THC detectable for hours after consumption
- Blood: THC present for hours to days depending on use frequency
- Urine: Inactive metabolites detectable for days to weeks
- Hair: Historical use detectable for months
However, detection doesn’t equal impairment. Understanding how long does THC stay in your body in a functionally impairing concentration requires examining real-world performance rather than merely chemical presence.
This issue was examined in the following study by Mastropietro et al., 2005, which investigated whether residual cognitive effects translate to observable driving dysfunction.
The Science of Cannabis Residual Effects
Research into cannabis residual effects examines whether cognitive changes persist after acute intoxication subsides. Understanding how long does THC stay in your body is essential when evaluating whether these subtle memory or reaction time differences could meaningfully impact real-world driving performance.
Results from the current study suggest that residual cognitive deficits of cannabis, if present, may not translate directly to observable dysfunction in real-world, over-learned activities such as driving. This finding challenges overly conservative recommendations suggesting drivers should abstain from operating vehicles for extended periods after cannabis consumption.
James Wigmore’s testimony in over 700 cases and peer-reviewed research on THC analysis provides forensic science foundations for understanding when cannabis actually impairs versus when it merely remains detectable in the body.
Simulated Driving Performance Research
The study used a STISIM M300WS-Console Driving Simulator System which included 3-screen, wide field-of-view monitors, steering wheel, accelerator, and brake pedals. The simulation included urban and rural driving segments and was of 25 minutes duration. The total composite drive score (CDS) was employed as a measure of driving ability and impairment.
This sophisticated simulation technology provides ecologically valid assessment of driving performance, measuring lane positioning, speed control, response to traffic signals, and crash avoidance—the real-world skills that matter for road safety.
The study was divided into 2 parts. The CDS of 118 male and 73 female cannabis-using participants were determined and compared with grams of cannabis used in the last 6 months, days since last cannabis use, and age of onset of cannabis use.
To ensure participants were not acutely impaired, researchers confirmed that oral fluid THC concentrations were below 5 ng/mL and breath alcohol was undetectable. This careful screening helps clarify how long does THC stay in your body without affecting driving performance, allowing the study to isolate residual effects from any acute intoxication.
Cannabis Use History and Driving Ability
The results of the first study showed that: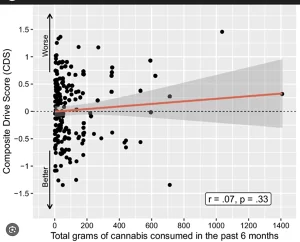
In study I, there was no relationship between CDS, its subjects, measures of cannabis use history, or demographic variables.
Despite examining 191 cannabis users with varying consumption patterns, the research found no correlation between how long THC stays in your body (measured through use history) and actual driving performance. Total grams consumed, recency of use, and age of onset showed no relationship to composite drive scores.
This finding suggests that concerns about long-term residual impairment may be unfounded for individuals who have allowed sufficient time for acute effects to subside. The data contradicts recommendations for 24-48 hour or even 28-day abstinence periods before driving.
In the second part of this paper, the CDS of 18 frequent cannabis users with the highest cannabis use intensity were compared to 12 matched, non-cannabis-using controls. These frequent users represented the population most likely to show residual effects if such effects genuinely impair driving.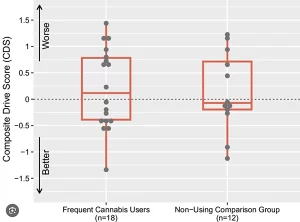
The current study also shows no evidence of short-term residual effects on simulated driving performance when comparing frequent cannabis users to healthy non-using comparison groups. Even the heaviest cannabis consumers performed equivalently to controls when oral fluid THC remained below 5 ng/mL.
Evidence-Based Guidelines for Safe Driving After Cannabis Use
The authors concluded:
In regular cannabis users who abstained for > 48 h and had oral fluid < 5 ng/mL, we found no evidence of residual cannabis effects on simulated driving performance.
These findings provide evidence-based guidance for answering how long does THC stay in your body in impairing concentrations. While THC metabolites may remain detectable much longer, functional impairment of driving ability appears to resolve within 48 hours for regular users, and likely sooner for occasional users.
Forensic toxicology expertise remains essential for interpreting drug testing results in traffic safety contexts, particularly when assessing how long does THC stay in your body and whether residual THC could pose any risk to driving safety. James Wigmore’s research contributions help distinguish between:
- Acute THC intoxication requiring immediate driving prohibition
- Residual THC presence without functional impairment
- Historical cannabis use irrelevant to current driving ability
Public health recommendations should reflect scientific evidence rather than overly conservative assumptions. The research demonstrates that:
Regular cannabis users who abstain for 48+ hours show no driving impairment. Oral fluid THC concentrations below 5 ng/mL indicate sufficient time has elapsed since consumption. Real-world driving performance returns to baseline despite detectable THC metabolites. Extended abstinence periods (24-48 hours or 28 days) lack scientific support for regular users.
These evidence-based guidelines balance genuine traffic safety concerns with avoiding unnecessary restrictions unsupported by performance data. Understanding how long THC stays in your body in functionally impairing versus merely detectable amounts allows for rational policy development.
Reference
Mastropietro, D.J., Omidi, L., Rogeberg, O., and Matthews, S.A., “Residual Effects of Cannabis Use on Simulated Driving Performance,” Journal of Psychopharmacology, 19(4): 358-364, 2005
Act Now: Protect Your Driving Rights
Leverage Forensic Science to Understand THC Evidence
James Wigmore’s forensic team continuously reviews and catalogs over 14,000 studies – giving you access to cutting-edge insights on THC detection, impairment markers, and driving safety research. Use this expertise to challenge claims based on unreliable or misinterpreted cannabis testing.
Get a Free Forensic Evaluation!Don’t let questionable THC evidence affect your safety record or legal standing. Contact us today.
How Long Does THC Stay in Your Body: FAQs
How long does THC stay in your body and affect driving?
Research shows regular cannabis users who abstain for over 48 hours with oral fluid THC below 5 ng/mL demonstrate no driving impairment. THC may remain detectable longer, but functional impairment resolves much sooner.
Can you drive safely 24 hours after using cannabis?
For regular users abstaining 48+ hours with oral fluid THC under 5 ng/mL, research found no evidence of residual cannabis effects on simulated driving performance compared to non-users.
Does cannabis use history affect current driving ability?
No relationship was found between cannabis use history (total grams consumed, recency of use, age of onset) and composite drive scores when oral fluid THC remained below 5 ng/mL.
What THC level indicates driving impairment?
The study used oral fluid THC concentration < 5 ng/mL as a threshold indicating no acute intoxication. Participants below this level showed no driving performance deficits compared to non-users.
Do frequent cannabis users drive worse than non-users?
Research comparing frequent cannabis users to matched non-using controls found no evidence of short-term residual effects on simulated driving performance when THC levels were below 5 ng/mL.
Should you wait 28 days to drive after using cannabis?
No scientific evidence supports 28-day waiting periods. Research found no residual driving impairment in regular users who abstained 48+ hours with oral fluid THC below 5 ng/mL.
How was driving ability measured in the cannabis research?
The study used a sophisticated STISIM M300WS driving simulator with 3-screen monitors, steering wheel, and pedals, measuring composite drive scores across 25-minute urban and rural segments.
Does THC detection mean driving impairment?
No. THC metabolites remain detectable far longer than they cause functional impairment. Detection in urine or hair doesn't indicate current impairment or compromised driving ability.
What do forensic toxicologists say about cannabis and driving?
Forensic experts like James Wigmore emphasize distinguishing acute THC intoxication from residual presence. Evidence shows driving performance returns to baseline despite detectable THC metabolites in regular users abstaining 48+ hours.
How many people were studied in the cannabis driving research?
The first study examined 191 cannabis users (118 male, 73 female). The second study compared 18 frequent cannabis users to 12 matched non-using controls using sophisticated driving simulation technology.
Recent News

How Long Does THC Stay in Your Body and Impact Rea...
How long does THC stay in your body, and more importantly, how long does it...
Read More
The Three-Headed Hydra at Work: Which Drug Poses t...
Workplace injury prevention requires understanding which substances actually increase accident risk. The three most destructive...
Read More
How Long Does Weed Stay in Your System? A Driver&#...
How long does weed stay in your system is a critical question for any cannabis...
Read More
Are Marijuana Smokers Safer Drivers than Drinkers?...
This is the first blog in the new area of drugs that I will be...
Read More